82 yo AAF was admitted to ICU for Afib with RVR. She has multiple comorbidities, among them a recent DVT and PE, for which Coumadin was started. Her INR is subtherapeutic and heparin IV is initiated after admission. She is lethargic and barely responsive to stimuli. Her code status is DNR-CCA.
PMH: AAA, thoracic aorta aneurysm, PE, DVT, colon CA S/P resection and colostomy, COPD, dementia
What happened?
Four days after admission, her platelet count decreased in half and blue discoloration of the toes was noted.


CBC in HIT; Coagulation panel in DVT and HIT
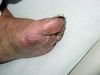
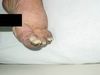
Peripheral thrombosis and emboli leading to skin necrosis in heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT)
What do you think is going on?
Heparin-induces thrombocytopenia (HIT).
HIT is a dangerous condition with a mortality rate of 50%, mainly due to thrombotic complications.
What would you do?
The treatment is with argatroban which is an anticoagulant requiring monitoring PTT in the same way as with heparin.
But the patient has thrombocytopenia and is at risk for bleeding, isn't she?
The thrombosis risk far outweighs the bleeding risk.


PTT monitoring in argatroban treatment
Antiplatelet antibodies were sent to the lab but the result is not reported immediately and that is why HIT is a clinical diagnosis.
What happened?
Heparin was stopped, argatroban was started and platelet count gradually increased. Duplex of LE showed an acute "on old" bilateral DVT.

Duplex of LE positive for DVT
Her mental status did not improve and the family members decided to convert the patient's code status to DNR-CC, according to her previously expressed wishes. Hospice care was called.
Final diagnosis: Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia with thrombosis.
PMH: AAA, thoracic aorta aneurysm, PE, DVT, colon CA S/P resection and colostomy, COPD, dementia
What happened?
Four days after admission, her platelet count decreased in half and blue discoloration of the toes was noted.


CBC in HIT; Coagulation panel in DVT and HIT


Peripheral thrombosis and emboli leading to skin necrosis in heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT)
What do you think is going on?
Heparin-induces thrombocytopenia (HIT).
HIT is a dangerous condition with a mortality rate of 50%, mainly due to thrombotic complications.
What would you do?
The treatment is with argatroban which is an anticoagulant requiring monitoring PTT in the same way as with heparin.
But the patient has thrombocytopenia and is at risk for bleeding, isn't she?
The thrombosis risk far outweighs the bleeding risk.


PTT monitoring in argatroban treatment
Antiplatelet antibodies were sent to the lab but the result is not reported immediately and that is why HIT is a clinical diagnosis.
What happened?
Heparin was stopped, argatroban was started and platelet count gradually increased. Duplex of LE showed an acute "on old" bilateral DVT.

Duplex of LE positive for DVT
Her mental status did not improve and the family members decided to convert the patient's code status to DNR-CC, according to her previously expressed wishes. Hospice care was called.
Final diagnosis: Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia with thrombosis.