88 yo AAF was admitted to the hospital with hematuria and anemia. The cystoscopy showed a bladder cancer and she had a cystectomy today.
She is on a vent post surgery and a pulmonolgy consult is called.
PMH: HTN, CRI
Medications: Atenolol
Physical exam:
Thin lady (5 kg) on vent, nonresponsive to verbal stimuli
VS 36.2-14-93-160/90
Chest: CTA (B)
CVS: Clear S1S2
Abdomen: Soft, ND, surgical dressing after the cystectomy
Extremities: no edema
Look at the ABG:


ABG shows respiratory alkalosis; CBC, CMP
Use the ARMADA mnemonic to work it up:
Alkalosis
Respiratory
Metabolic acidosis - HCO3 19 due to CRI
Anion gap - we will look at the BMP
Admixed disorder? - yes, respiratory alkalosis and an old, well-known metabolic acidosis due to CRI
Delta AG
What to do?
She is hyperventilating
TV 450 is too big for her - she is is just 50 kg and 5 feet tall. If you use TV 7 cc/kg, the correct TV now is 350 cc/hr.
Also, she does not need FiO2 50% now, her PaO2 is 118 mm Hg.
What was done?
TV was decreased to 350 cc
FiO2 was decreased to 40%
We will recheck the ABG in 30 min to 1 hour.
Do not forget to check the CXR.
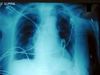


Check out the 3 tubes on this CXR - right subclavian TLC, ET and NGT; CXR report
Check all the tubes. ET is at the level of the clavicles, 5 cm above the carina and has to be advanced 2 cm. The ideal ET position is between the clavicles and the carina.
What about the other tubes?
NGT is in the stomach. The central line though is in the IJ vein and needs to be repositioned.
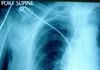
On this close-up view, you can clearly see that the R TLC goes in the IJ vein instead of going down the R subclavian vein. The TLC catheter needs to be repositioned as soon as possible. The ET at the level of the clavicles is too high. The patient may extubated herself of the ET is too high, it needs to be advanced.

Close-up view of the NGT in the stomach
The order should be: Advance ET 2 cm, repeat the CXR.
Before that, you need to replace the central line. After that, you need to order a CXR to check the position of both the central line and the ET.
Can this patient be extubated?
No.
ABG is not that bad but she is unresponsive and she cannot protect her airway now.
Why is the patient unresponsive now?
The causes may by a myriad
This is an elderly patiend who is just after major surgery. She received Fentanyl and MS and this may explain the change in mental status.
You also need to R/O ischemia and intracranial process.
Final diagnosis: Respiratory alkalosis due to hyperventilation
What did we learn from this case?
Calculate the TV according to the IBW
Do not extubate unresponsive patients (unless the family decides on terminal weaning in accordance with the patien't wishes).
Check the position of all tubes on a CXR of an ICU patient.
She is on a vent post surgery and a pulmonolgy consult is called.
PMH: HTN, CRI
Medications: Atenolol
Physical exam:
Thin lady (5 kg) on vent, nonresponsive to verbal stimuli
VS 36.2-14-93-160/90
Chest: CTA (B)
CVS: Clear S1S2
Abdomen: Soft, ND, surgical dressing after the cystectomy
Extremities: no edema
Look at the ABG:


ABG shows respiratory alkalosis; CBC, CMP
Use the ARMADA mnemonic to work it up:
Alkalosis
Respiratory
Metabolic acidosis - HCO3 19 due to CRI
Anion gap - we will look at the BMP
Admixed disorder? - yes, respiratory alkalosis and an old, well-known metabolic acidosis due to CRI
Delta AG
What to do?
She is hyperventilating
TV 450 is too big for her - she is is just 50 kg and 5 feet tall. If you use TV 7 cc/kg, the correct TV now is 350 cc/hr.
Also, she does not need FiO2 50% now, her PaO2 is 118 mm Hg.
What was done?
TV was decreased to 350 cc
FiO2 was decreased to 40%
We will recheck the ABG in 30 min to 1 hour.
Do not forget to check the CXR.



Check out the 3 tubes on this CXR - right subclavian TLC, ET and NGT; CXR report
Check all the tubes. ET is at the level of the clavicles, 5 cm above the carina and has to be advanced 2 cm. The ideal ET position is between the clavicles and the carina.
What about the other tubes?
NGT is in the stomach. The central line though is in the IJ vein and needs to be repositioned.

On this close-up view, you can clearly see that the R TLC goes in the IJ vein instead of going down the R subclavian vein. The TLC catheter needs to be repositioned as soon as possible. The ET at the level of the clavicles is too high. The patient may extubated herself of the ET is too high, it needs to be advanced.

Close-up view of the NGT in the stomach
The order should be: Advance ET 2 cm, repeat the CXR.
Before that, you need to replace the central line. After that, you need to order a CXR to check the position of both the central line and the ET.
Can this patient be extubated?
No.
ABG is not that bad but she is unresponsive and she cannot protect her airway now.
Why is the patient unresponsive now?
The causes may by a myriad
This is an elderly patiend who is just after major surgery. She received Fentanyl and MS and this may explain the change in mental status.
You also need to R/O ischemia and intracranial process.
Final diagnosis: Respiratory alkalosis due to hyperventilation
What did we learn from this case?
Calculate the TV according to the IBW
Do not extubate unresponsive patients (unless the family decides on terminal weaning in accordance with the patien't wishes).
Check the position of all tubes on a CXR of an ICU patient.