54 yo CF with PMH of end-stage COPD fell and injured her left shoulder. She was taken to the nearest ER and received Toradol for pain. She became lethargic and was given Naloxone which made her agitated. She was given Ativan and shortly after that she became unresponsive.
PMH: COPD on home O2 - 5 l/min, DVT S/P IVC filter, HTN, heroin abuse on methadone now
Medications: Lasix, Prednisone, aerosols, Coumadin, Methadone
SH: Lives with her husband, smoker - 40 pck-yrs, heroin abuse in the past
Physical examination:
Thin lady, lethargic
VS 36.7-24-102-120/60
SpO2 90% on 5 L
Chest: decreased AE (B)
CVS: Clear S1S2
Abdomen: Soft, NDT, ND
Extremities: chronic stasis dermatitis (B)
What do you think is going on?
Respiratory depression from BDZ? Or oipoids?
What would you do?
She needs ABG stat.
Call a respiratory therapist because an intubation may be needed.
Order CBCD, CMP, CPP x 2 q 8 hr, EKG, CXR.
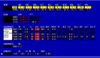

CBC and CMP; Urine toxic screen

ABGs in a patient with COPD and BDZ overdose
What happened?
Flumazenil 0.2 mg IV x 3 was given with an immediate response. BiPAP 16/6 was started and ABG was repeated.
Her mental status improved and she avoided intubation.
After 2 days treatment with Solu-Medrol and aerosols, she was discharged home.
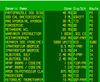
Medications used
Final diagnosis: Respiratory depression due to BDZ in COPD
What did we learn from this case?
BDZ are contraindicated in COPD patients because they can induce a severe respiratory depression.
The antagonist drug of choice is Flumazenil. The beneficial effect is usually immediate (similar to Naloxone in opioid overdose). If the patient does not respond to repeated doses of Flumazenil, consider other diagnoses than BDZ overdose.
BiPAP can help avoid intubation in respiratory failure. Do not use it in unresponsive patients because of the aspiration risk. There should be a noticeable improvement in ABG within 30 min of BiPAP treatment.
PMH: COPD on home O2 - 5 l/min, DVT S/P IVC filter, HTN, heroin abuse on methadone now
Medications: Lasix, Prednisone, aerosols, Coumadin, Methadone
SH: Lives with her husband, smoker - 40 pck-yrs, heroin abuse in the past
Physical examination:
Thin lady, lethargic
VS 36.7-24-102-120/60
SpO2 90% on 5 L
Chest: decreased AE (B)
CVS: Clear S1S2
Abdomen: Soft, NDT, ND
Extremities: chronic stasis dermatitis (B)
What do you think is going on?
Respiratory depression from BDZ? Or oipoids?
What would you do?
She needs ABG stat.
Call a respiratory therapist because an intubation may be needed.
Order CBCD, CMP, CPP x 2 q 8 hr, EKG, CXR.


CBC and CMP; Urine toxic screen

ABGs in a patient with COPD and BDZ overdose
What happened?
Flumazenil 0.2 mg IV x 3 was given with an immediate response. BiPAP 16/6 was started and ABG was repeated.
Her mental status improved and she avoided intubation.
After 2 days treatment with Solu-Medrol and aerosols, she was discharged home.

Medications used
Final diagnosis: Respiratory depression due to BDZ in COPD
What did we learn from this case?
BDZ are contraindicated in COPD patients because they can induce a severe respiratory depression.
The antagonist drug of choice is Flumazenil. The beneficial effect is usually immediate (similar to Naloxone in opioid overdose). If the patient does not respond to repeated doses of Flumazenil, consider other diagnoses than BDZ overdose.
BiPAP can help avoid intubation in respiratory failure. Do not use it in unresponsive patients because of the aspiration risk. There should be a noticeable improvement in ABG within 30 min of BiPAP treatment.