From BMJ:
In a child, unusual bruising or bleeding out of proportion to the injury sustained should be investigated.
All children under investigation for easy bruising or a bleeding tendency should have:
- full blood count
- blood film (peripheral smear)
- coagulation screen including a thrombin time, in addition to a Von Willebrand factor assay and assays of factors VIII and IX
This is to ensure that mild forms of haemophilia are excluded even if the activated partial thromboplastin time is normal
In 30% of cases of haemophilia, there is no family history: it arises secondary to new genetic mutations
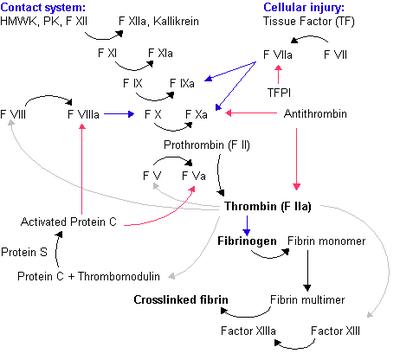
The coagulation cascade. Black arrow - conversion/activation of factor. Red arrows - action of inhibitors. Blue arrows - reactions catalysed by activated factor. Grey arrow - various functions of thrombin. Image source: Wikipedia
References:
Investigating easy bruising in a child. Anderson and Thomas 341, BMJ.
In a child, unusual bruising or bleeding out of proportion to the injury sustained should be investigated.
All children under investigation for easy bruising or a bleeding tendency should have:
- full blood count
- blood film (peripheral smear)
- coagulation screen including a thrombin time, in addition to a Von Willebrand factor assay and assays of factors VIII and IX
This is to ensure that mild forms of haemophilia are excluded even if the activated partial thromboplastin time is normal
In 30% of cases of haemophilia, there is no family history: it arises secondary to new genetic mutations

The coagulation cascade. Black arrow - conversion/activation of factor. Red arrows - action of inhibitors. Blue arrows - reactions catalysed by activated factor. Grey arrow - various functions of thrombin. Image source: Wikipedia
References:
Investigating easy bruising in a child. Anderson and Thomas 341, BMJ.